 |
Core Concepts | .9 | .11 | .12 | .13 | .14 | .15 | .16 | .17 | .18 |
3.16 Simulations
Student led teaching on Simulations. Learn how simulations allow for experimentation and analysis in a controlled, virtual environment.
Simulations
A simulation is the use of a computer software to represent the dynamic responses of one system by the behaviour of another system modeled after it. A simulation uses a mathematical descriptions, or models, of a real system in the form of a computer program.
College Board Essential Knowledge
Simulation are absractions of more complex objects or phenomena for a specific purpose
- Mimic Real World Events
- Allows investigation of phenomenons without contraints of the Real World
- Helps you draw accurate inferences
Simulations utilize varying sets of values to reflect the changings states of a phenomenon
- simulations can simplfly things for functionality
- Simulations can contain bias from real world elements, that were chosen to be included or excluded
Simulations work best when the real world experemnts are too impractical or time consuming. For example, simulating how different cars behave when they crash, would be much better than crashng actual cars in the real world, which would be expensive and dangerous.
Rolling the Dice
Simulating something like a dice roll in real life would require accounting for things like: weight, flaws in design, thrust, and gravity.
- KEEP IT SIMPLE! just use a random-number generator! Ignore minor causes of variablility
Random
- “Random” is a built-in python function that allow the user to draw a random value from a set range.
- A Random Number Generator (RNG) is a common simulation that selects a random value from an array.
- The following code cell utilizes “random” to select a number from 1 to 100.
#imports random module so we can use it in our code
import random
#sets variable random_number as a random number between 1 and 100
random_number = random.randint(1, 100)
#Printing out your random Number
print(random_number)
88
More complex usage of “random”; Coin Toss Simulation
import random
def flip_coin():
return random.choice(["Heads", "Tails"])
def coin_flip_simulation(num_flips):
heads_count = 0
tails_count = 0
for _ in range(num_flips):
result = flip_coin()
if result == "Heads":
heads_count += 1
else:
tails_count += 1
return heads_count, tails_count
if __name__ == "__main__":
num_flips = 1000 #This is the number of coin flips you want to simulate
heads, tails = coin_flip_simulation(num_flips)
print("Number of Heads: "+ str(heads))
print("Number of Tails: " + str(tails))
print("Heads Probability: "+ str({heads / num_flips}))
print("Tails Probability: "+ str({tails / num_flips}))
Number of Heads: 483
Number of Tails: 517
Heads Probability: {0.483}
Tails Probability: {0.517}
Algorithms
Simulations often utilize algorithms and equations to perform tasks because simulations don’t always have the same output
- the output of a simulation depends on the input
An algorithm is a finite sequence of instructions used to solve problems or perform computations.
- commonly used alongside functions
Example Algorithm in a function
#Defining Function
def algorithm(input):
#Manipulating input and preparing it for the output.
output = input+2
#Return the output
return output
#Call the Function to start the algorithm
algorithm(5)
7
Mathematics
- Math can also prove to be very useful in certain types of situations.
- Commonly used along with Algorithms when simulating various things

Using Loops in Simulations
For loops can also be used in simulations
- They can simulate events that repeat but don’t always have the same output
Example For Loop
#Creating For Loop to repeat 4 times
for i in range(4):
#Action that happens inside for loop
print("This is run number: " + str(i))
This is run number: 0
This is run number: 1
This is run number: 2
This is run number: 3
Sample Quiz
Here is a sample quiz to test your knowledge of simulations.
T or F
- A simulation will always have the same result. (False) T or F
- A simulation investigates a phenomenom without real-world constraints of time, money, or safety. (True) T or F
- A simulation has results which are more accurate than an experiment. (False) T or F
- A simulation can model real-world events that are not practical for experiments (True)
Hacks
Review each of the following and produce….
- Simulate how long an object will fall for using an algorithm, with user-inputed variables for height dropped. Use the following formula as a reference.
- t = time (output)
- h = height dropped from (input)
- g = constant (given, 9.81)
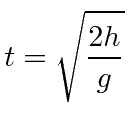
- Given initial parameters for a car simulation, including its initial speed, acceleration rate, deceleration rate, maximum speed, and initial distance, write a program to simulate the car’s journey and determine the final speed, distance covered, and time taken before it either covers 1000 meters or slows down to below 5 m/s?
- speed = 0 (Initial speed)
- acceleration = 2 (Acceleration rate in m/s^2)
- deceleration = 1 (Deceleration rate in m/s^2)
- max_speed = 60 (Maximum speed in m/s)
- distance = 0 (Initial distance)
- time = 0 (Initial time)

